Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It is the most common cause of dementia, impacting millions of individuals and their families worldwide. While there is currently no cure, advancements in treatment options can significantly improve quality of life and slow disease progression. At the Neurology and Pain Management Clinic (NPMC), Dr. Gautam Arora and his team specialize in providing personalized care for Alzheimer’s patients and support for their caregivers.
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
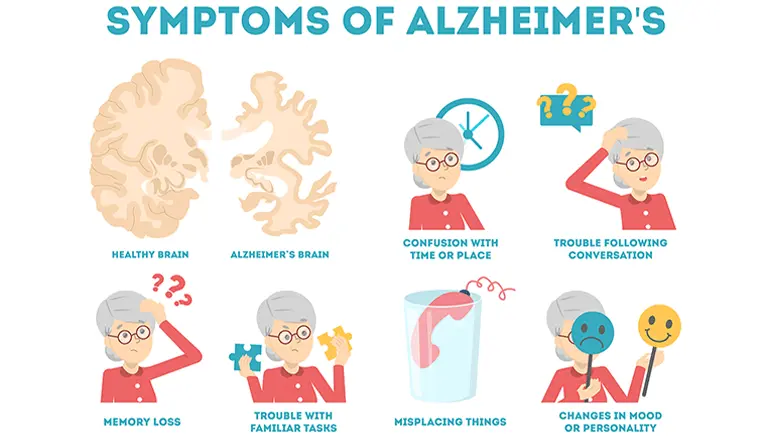
Alzheimer’s is a condition characterized by the deterioration of brain cells, leading to memory loss, confusion, and difficulties in completing daily tasks. Its hallmark features include:
- Amyloid Plaques: Clumps of protein that disrupt communication between brain cells.
- Neurofibrillary Tangles: Twisted fibers of protein that impair nutrient transport within brain cells.
- Brain Atrophy: Shrinking of brain tissues due to cell death.
Symptoms typically begin with mild memory lapses and progress to severe cognitive and functional impairments over time.
Current Treatment Goals
The primary goals of Alzheimer’s treatment are to:
- Slow Disease Progression: Delay the advancement of symptoms.
- Improve Quality of Life: Enhance cognitive function and daily living abilities.
- Manage Behavioral Changes: Address mood swings, agitation, and confusion effectively.
Early Diagnosis is Key
Dr. Gautam Arora emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis. Timely intervention allows for better management of symptoms and planning for the future.
Medications for Alzheimer’s
Several medications are available to treat Alzheimer’s symptoms. These include:
1. Cholinesterase Inhibitors
These drugs enhance communication between nerve cells by preventing the breakdown of acetylcholine, a key neurotransmitter. Common examples include:
- Donepezil
- Rivastigmine
- Galantamine
2. NMDA Receptor Antagonists
Memantine is a medication that regulates glutamate activity, protecting brain cells from damage caused by overstimulation. It is often used in moderate to severe stages of Alzheimer’s.
3. Combination Therapies
Combining cholinesterase inhibitors with memantine has shown promising results in managing symptoms more effectively.
Non-Medication Interventions
In addition to medications, NPMC offers holistic care strategies that focus on improving patients’ overall well-being:
1. Cognitive Stimulation Therapy (CST)
CST involves activities and exercises designed to enhance memory, problem-solving, and communication skills.
2. Lifestyle Modifications
Dr. Arora often recommends:
- Regular Physical Activity: Promotes brain health by improving blood flow.
- Healthy Diet: A Mediterranean diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3s supports cognitive function.
- Social Engagement: Interaction with others can delay cognitive decline.
3. Behavioral Therapy
Addressing behavioral symptoms like aggression or anxiety through structured routines and caregiver support.
The Role of Caregivers
Caregivers play a crucial role in managing Alzheimer’s patients. At NPMC, Dr. Arora provides counseling and resources for caregivers to help them navigate the challenges of caregiving, including strategies for effective communication and stress management.
Advances in Alzheimer’s Research
Ongoing research is bringing hope to Alzheimer’s patients and their families. Breakthroughs include:
- Biological Treatments: Therapies targeting amyloid plaques and tau tangles.
- Gene Therapy: Experimental treatments focusing on altering genetic risk factors.
- Digital Health Tools: Wearable devices and apps that monitor cognitive function and health metrics.
Conclusion